Need Help?
FAQs – DM & MB Plant
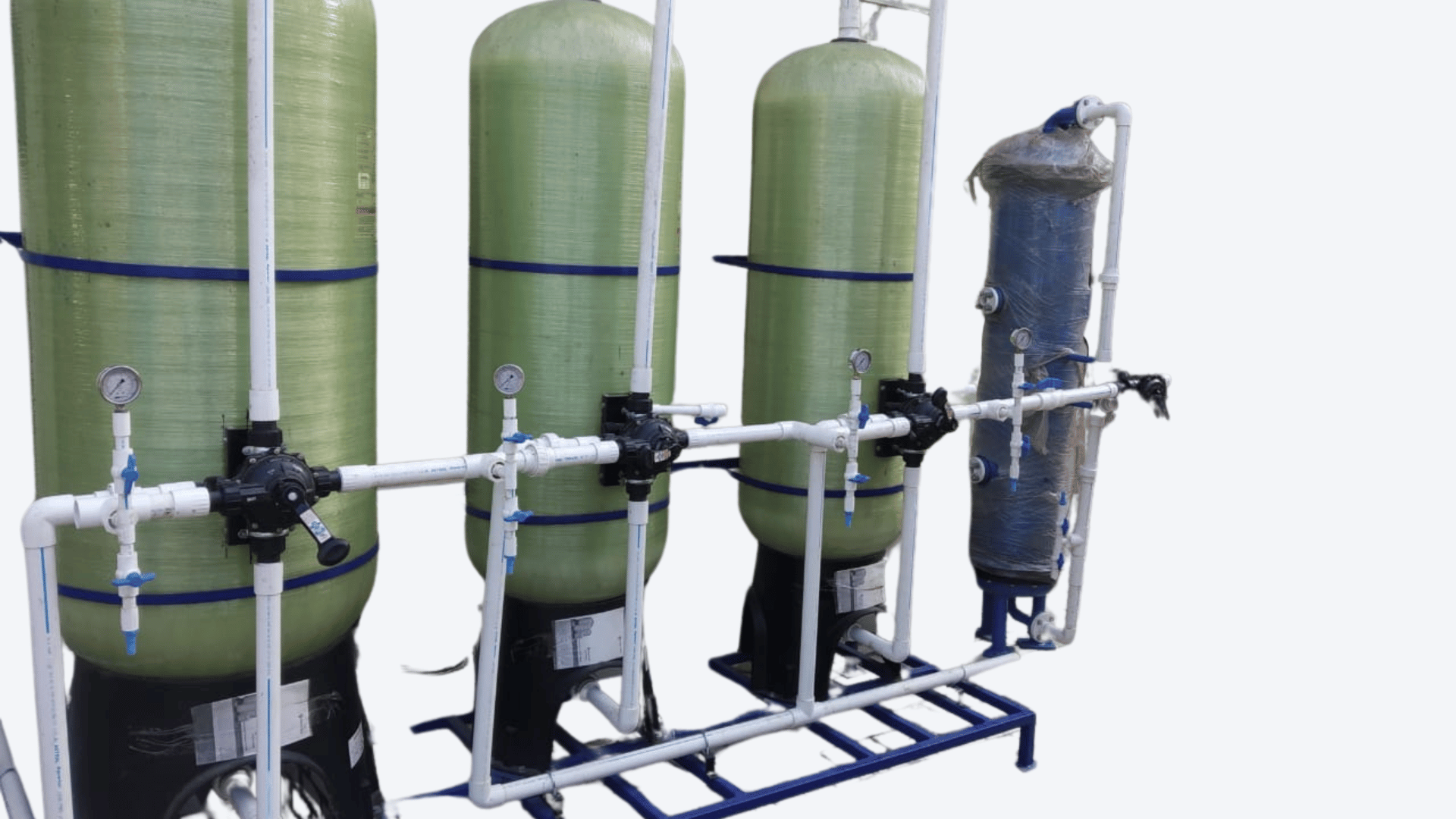
1. What is a Demineralization Plant ( DM )t used for?
A DM Demineralization Plant ( DM ) is used to produce deionized water by removing dissolved salts, making it ideal for industrial, chemical, and power generation processes.
2. What makes RO water different from Demineralization Plant ( DM ) water?
RO water removes 90–98% of TDS using membranes, while Demineralization Plant ( DM ) water removes nearly 100% of ions using ion exchange resins. DM water has lower conductivity and is preferred where ultra-pure water is needed.
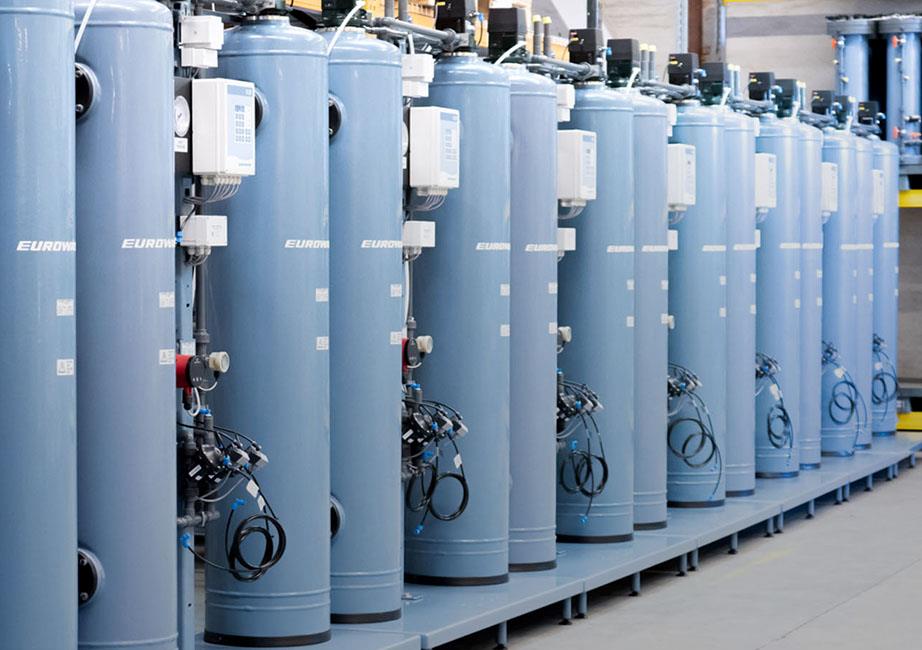
3. What is a Mixed Bed (MB) unit?
A Mixed Bed unit is a polishing step in a DM system containing both cation and anion resins. It further purifies water to reach ultra-low TDS and conductivity levels, often used in final rinse or lab-grade water applications.
4. Is Demineralization Plant ( DM ) water safe for drinking?
No. Demineralization Plant ( DM ) water lacks essential minerals and may affect the body’s electrolyte balance. It is not safe for human consumption and is intended for industrial and technical uses only.
5. How often do the resins in a Demineralization Plant ( DM ) need to be regenerated?
Regeneration frequency depends on water quality and usage volume. On average, resins may need regeneration after treating 5,000 to 30,000 liters of water, using acid and alkali solutions.
6. What is the conductivity of Demineralization Plant ( DM ) water?
Properly treated Demineralization Plant water has conductivity levels <10 µS/cm, and when polished with a Mixed Bed unit, it can go as low as 0.1–1.0 µS/cm.
7. What chemicals are used for regeneration in a Demineralization Plant ( DM )?
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) for cation resin
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) for anion resin
- The resin’s ability to exchange ions is restored by these substances.
8. Can a Demineralization Plant ( DM ) be used with borewell or well water?
Yes, but it’s advisable to use pre-treatment (sand filter, softener, or RO) before the Demineralization Plant ( DM ) to remove turbidity, hardness, or organic impurities for improved performance and resin life.
9. Which sectors make use of Demineralization Plant ( DM ) & MB water systems?
Industries include pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, chemical processing, electronics, hospitals, research labs, and power plants.
10. What capacity Demineralization Plant ( DM ) are available?
We offer Demineralization Plant in a wide range: 500 LPH to 20,000+ LPH, with tailored options based on feed water quality and process needs.