Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between STP and ETP plants?
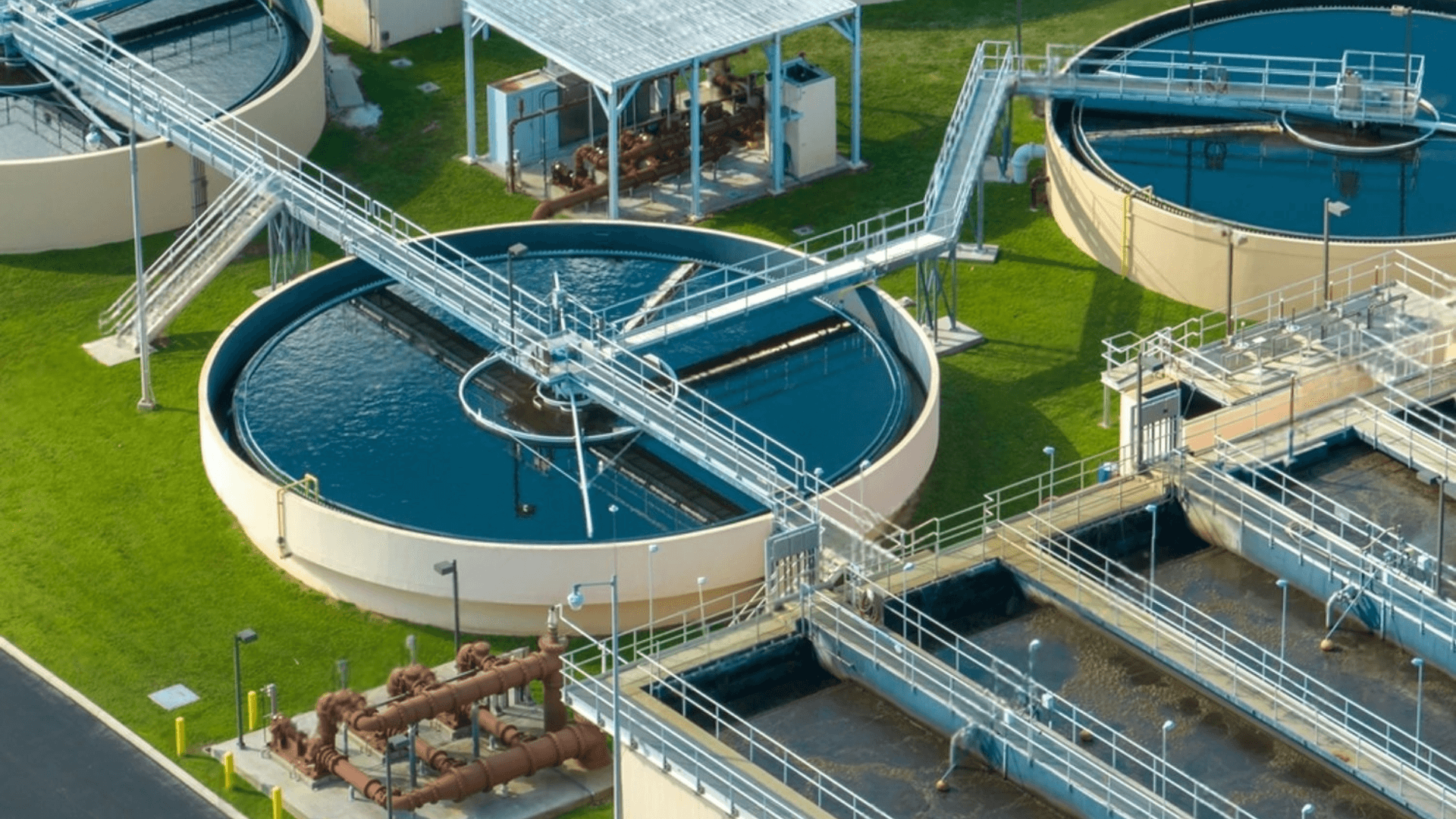
STP (Sewage Treatment Plant) is used to treat domestic sewage from residential and commercial buildings, while ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant) is used for treating industrial wastewater that contains harmful chemicals and pollutants.
2. How does a sewage treatment plant (STP) work?
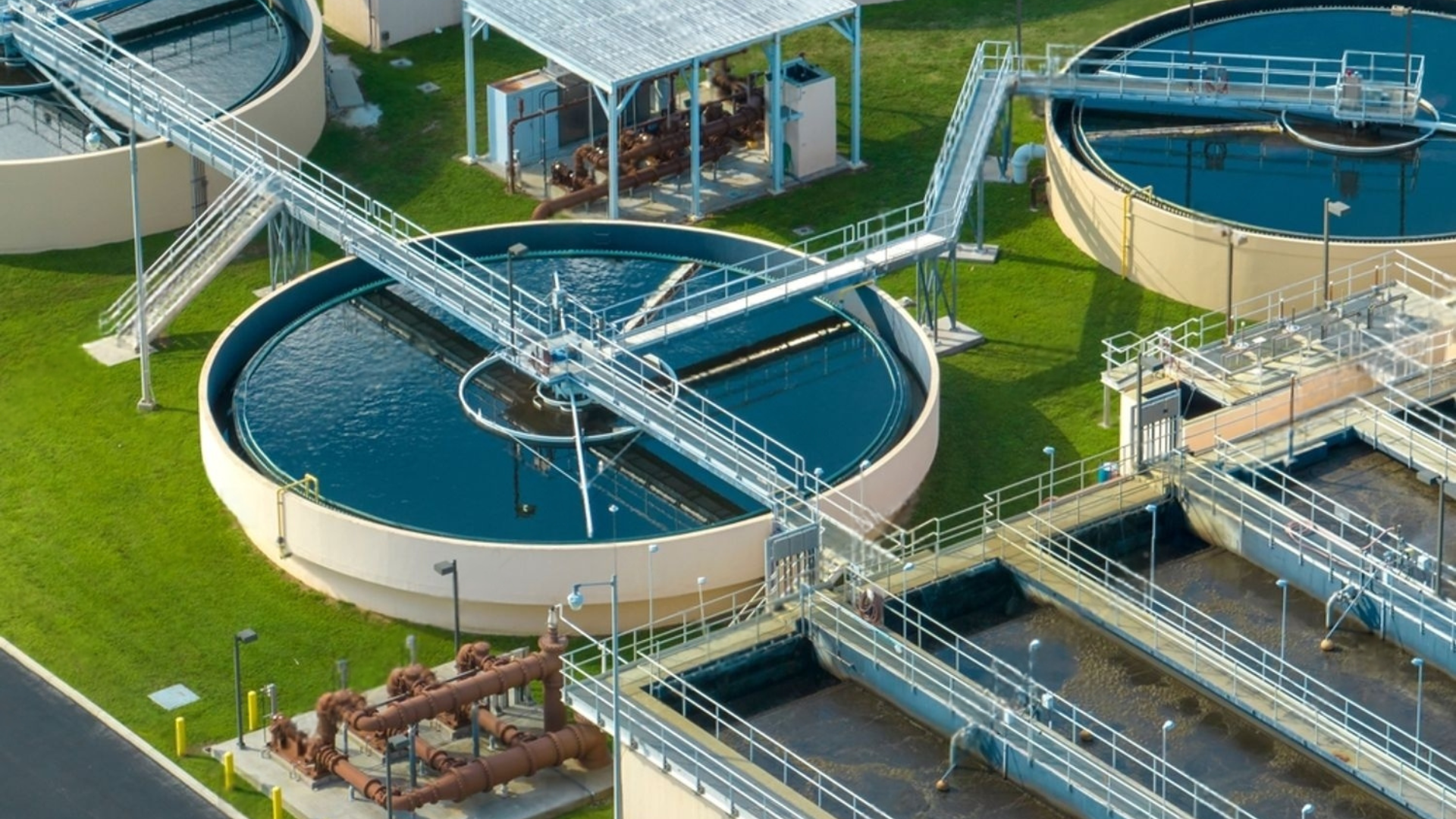
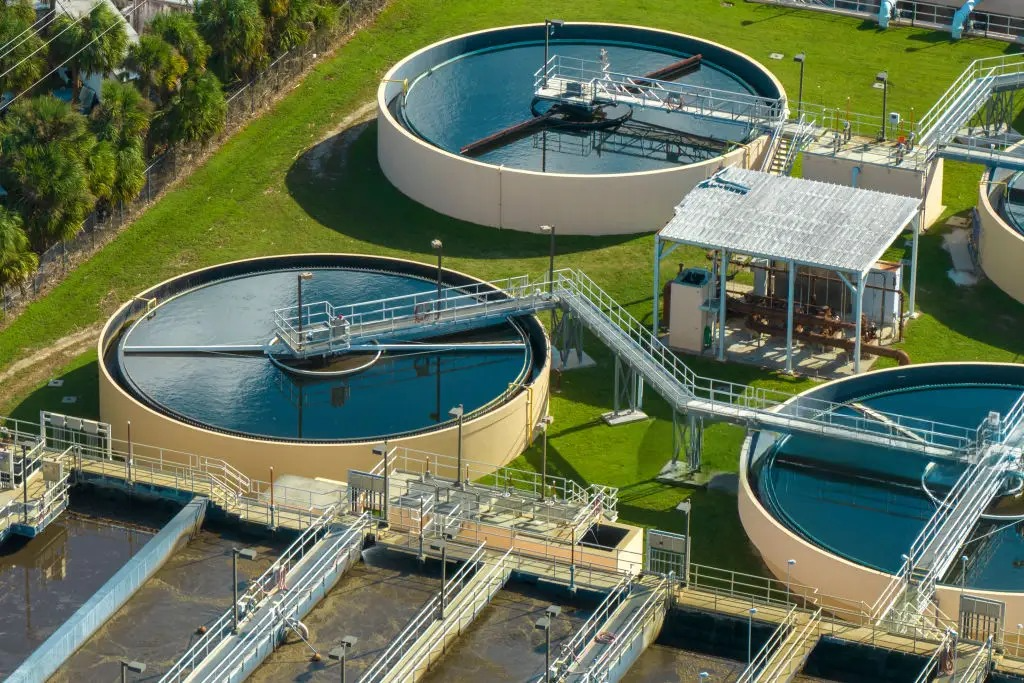
An STP works by removing contaminants from wastewater through processes like screening, aeration, sedimentation, and disinfection, making the water safe for reuse or discharge into the environment.
3. Why is an Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) important for industries?
An ETP is essential for industries to treat toxic wastewater, comply with environmental laws, reduce pollution, and avoid penalties from pollution control boards.
4. What is the capacity of a 100 KLD STP plant and where is it used?
A 100 KLD (Kilolitres per Day) STP plant treats 100,000 liters of sewage daily and is ideal for apartment complexes, commercial buildings, hotels, schools, and hospitals.
5. Can treated water from STP or ETP be reused?
Yes, treated water from both STP and ETP can be reused for non-potable purposes like gardening, flushing, construction, and industrial processes—reducing freshwater demand.
6. Is it mandatory to install an STP in residential projects in India?
Yes, as per CPCB and SPCB guidelines, residential and commercial projects exceeding a certain size must install STPs to ensure proper sewage treatment and environmental compliance.